Cyber Insurance Essential Digital Age Protection
Defining Cyber Insurance
Cyber insurance is a specialized type of insurance policy designed to protect businesses and individuals from the financial and operational consequences of cyberattacks and data breaches. It acts as a crucial safety net in today’s increasingly digital world, where the risk of cyber threats is ever-present. Unlike traditional insurance, cyber insurance focuses on the unique vulnerabilities and exposures associated with the digital landscape.
Cyber insurance policies typically comprise several core components. These components work together to provide comprehensive protection against a wide range of cyber-related incidents. The specific coverage offered can vary significantly depending on the policy and the insurer.
Core Components of a Cyber Insurance Policy
A typical cyber insurance policy will include coverage for several key areas. First, it often covers the costs associated with data breach response, including legal fees, public relations expenses, and credit monitoring services for affected individuals. Secondly, many policies provide coverage for business interruption losses resulting from a cyberattack that disrupts operations. This can include lost revenue and extra expenses incurred to restore services. Thirdly, cyber insurance can cover the costs of restoring damaged systems and data, a process that can be both time-consuming and expensive. Finally, it may offer liability protection against lawsuits stemming from a data breach or other cyber incident. The specific coverage amounts and limitations will be detailed in the policy document.
Types of Cyber Threats Covered
Cyber insurance policies cover a broad spectrum of cyber threats. These threats can be broadly categorized into several types. First, malware attacks, including ransomware, viruses, and Trojans, are frequently covered. These attacks can encrypt data, steal sensitive information, or disrupt operations. Secondly, phishing and social engineering attacks, which exploit human error to gain unauthorized access to systems or data, are often included in coverage. Thirdly, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, which overwhelm systems and make them inaccessible, are also commonly covered. Fourthly, data breaches resulting from hacking, employee negligence, or other causes are often a significant component of cyber insurance coverage. Finally, many policies extend coverage to extortion attempts related to data breaches or system disruptions. The specific threats covered will depend on the chosen policy and its endorsements.
Comparison of Cyber Insurance Providers and Their Offerings
The cyber insurance market is diverse, with numerous providers offering a range of policies and coverage options. Providers differ in their underwriting practices, the types of businesses they insure, the specific threats they cover, and the premium costs they charge. For example, some insurers specialize in specific industries, such as healthcare or finance, offering tailored policies to address the unique risks faced by those sectors. Others may offer broader coverage across a wider range of industries. It is crucial to compare several providers and their offerings before selecting a policy. Factors to consider include the policy’s coverage limits, deductibles, exclusions, and the insurer’s financial strength and reputation. It’s recommended to seek professional advice from an insurance broker specializing in cyber insurance to help navigate the market and select the most appropriate policy for your specific needs and risk profile. This ensures that you obtain adequate protection without overspending.
Identifying Digital Age Risks
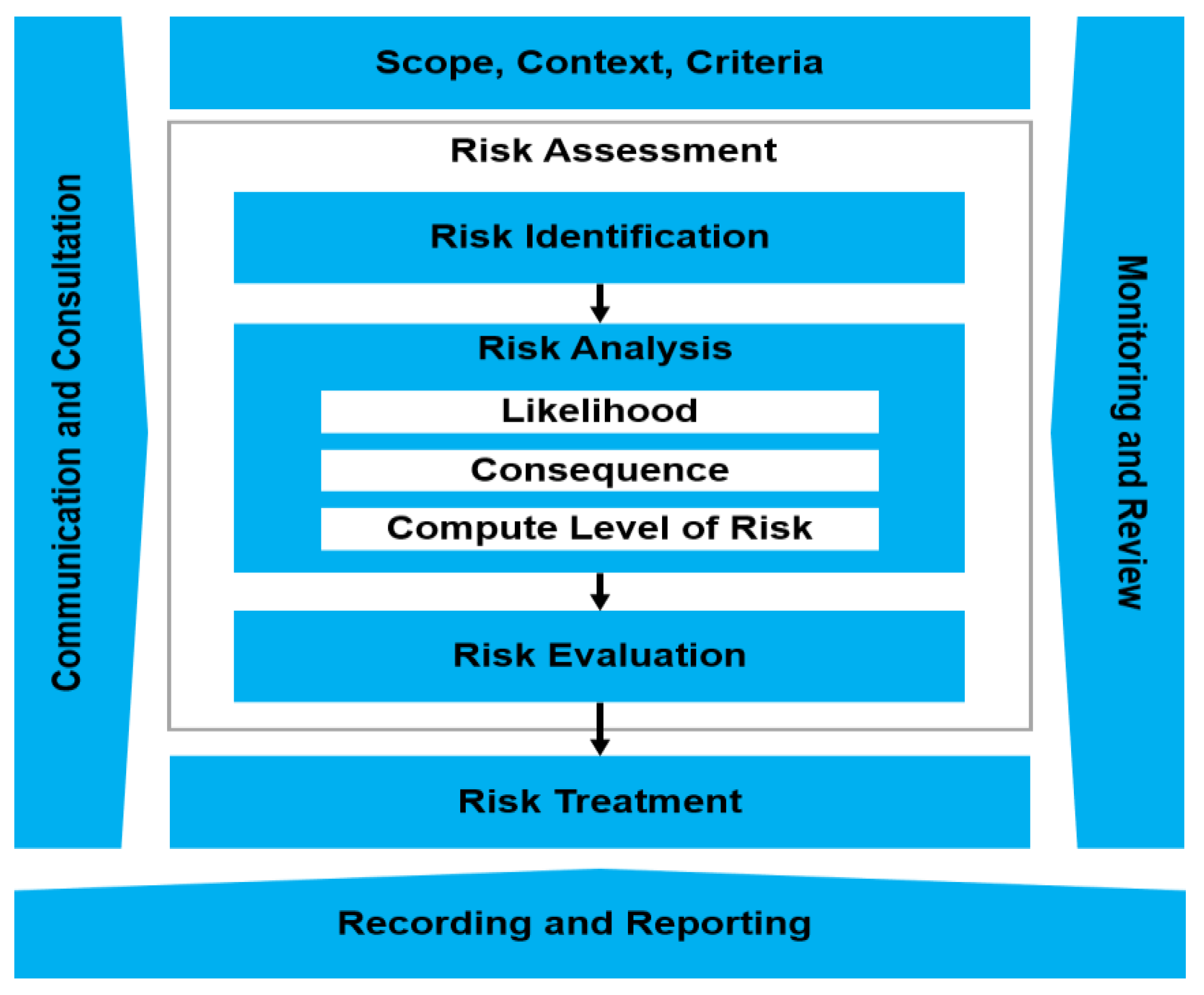
The digital age, while offering unprecedented opportunities, presents a growing landscape of cyber threats that businesses of all sizes must navigate. Understanding these risks is crucial for implementing effective cybersecurity measures and securing appropriate insurance coverage. Ignoring these risks can lead to devastating financial and reputational consequences. This section will Artikel the most prevalent cyber threats and illustrate the potential damage they can inflict.
Cyberattacks are increasingly sophisticated and pervasive, targeting businesses across various industries. The financial and reputational implications of a successful attack can be catastrophic, impacting not only immediate financial losses but also long-term stability and public perception. The cost of recovery, including legal fees, regulatory fines, and the loss of customer trust, can far exceed the immediate financial damage caused by the attack itself.
Prevalent Cyber Threats Facing Businesses
Five of the most common and impactful cyber threats facing businesses today include ransomware, phishing attacks, data breaches, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, and malware infections. These threats vary in their methods of attack and their ultimate objectives, but they all pose significant risks to a company’s operations and bottom line.
Financial and Reputational Damage from Cyberattacks
The financial repercussions of a cyberattack can be substantial, encompassing direct costs such as system recovery, data restoration, and incident response services. Indirect costs can be even more significant, including lost productivity, business disruption, legal fees, regulatory fines, and the cost of compensating affected customers. Beyond financial losses, a cyberattack can severely damage a company’s reputation, leading to a loss of customer trust, decreased market share, and difficulty attracting investors. This reputational damage can linger for years, even after the immediate crisis has been resolved.
Examples of Real-World Cyber Incidents and Their Consequences
Several high-profile cyber incidents demonstrate the devastating impact of cyberattacks. These examples highlight the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures and comprehensive cyber insurance coverage to mitigate potential losses.
| Type of Attack | Affected Organization | Financial Impact | Reputational Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ransomware | Colonial Pipeline | $4.4 million ransom payment; millions more in operational costs and cleanup | Significant damage to reputation, impacting public trust and fuel prices. |
| Data Breach | Equifax | Over $700 million in costs related to legal settlements, regulatory fines, and remediation | Severe reputational damage, leading to a decline in stock price and customer churn. |
| Phishing | Various small businesses | Varies greatly, from minor financial losses to complete business closure. | Damage to reputation and customer trust, particularly if sensitive customer data is compromised. |
| DoS Attack | Various online retailers | Loss of revenue due to website downtime, potentially impacting sales and customer satisfaction. | Negative impact on brand image and customer loyalty. |
Assessing Cyber Risk Exposure
Understanding your organization’s vulnerability to cyberattacks is crucial for effective risk management and the selection of appropriate cyber insurance coverage. A thorough assessment helps identify weaknesses and prioritize mitigation efforts, ultimately reducing your exposure to financial and reputational damage. This process involves examining various aspects of your digital infrastructure and operational procedures.
A comprehensive cyber risk assessment goes beyond simply identifying potential threats. It involves analyzing the likelihood of those threats materializing and the potential impact should a breach occur. This allows for a prioritized approach to mitigation, focusing resources on the most critical vulnerabilities. The following sections provide tools and guidance to help you conduct such an assessment.
Cyber Risk Assessment Questionnaire
This questionnaire helps businesses identify potential vulnerabilities. Answering honestly and comprehensively will provide a clearer picture of your risk profile. Remember, this is a starting point; a professional assessment may be necessary for a more in-depth analysis.
| Question | Yes | No | N/A |
|---|---|---|---|
| Do you have a robust password policy in place, including multi-factor authentication? | |||
| Are your software and operating systems regularly updated with security patches? | |||
| Do you conduct regular security awareness training for your employees? | |||
| Do you have a documented incident response plan? | |||
| Is your network regularly scanned for vulnerabilities? | |||
| Do you have a system for monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity? | |||
| Do you regularly back up your data and store it securely offsite? | |||
| Do you have a policy for handling sensitive customer data? | |||
| Do you use encryption to protect sensitive data both in transit and at rest? | |||
| Do you have a process for vetting third-party vendors and their security practices? |
Conducting a Thorough Cyber Risk Assessment
A structured approach is essential for a thorough cyber risk assessment. This involves a systematic process of identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential risks.
- Identify Assets: Catalog all valuable digital assets, including hardware, software, data, and intellectual property.
- Identify Threats: List potential threats, such as malware, phishing attacks, denial-of-service attacks, and insider threats.
- Assess Vulnerabilities: Identify weaknesses in your systems and processes that could be exploited by threats.
- Analyze Risks: Determine the likelihood and potential impact of each threat exploiting a vulnerability. This often involves assigning a risk score (e.g., low, medium, high).
- Develop Mitigation Strategies: Artikel strategies to reduce the likelihood or impact of identified risks. This might include implementing security controls, developing incident response plans, or purchasing insurance.
- Implement and Monitor: Implement the chosen mitigation strategies and regularly monitor their effectiveness.
Best Practices for Mitigating Cyber Risks
Implementing robust security measures is crucial for minimizing your cyber risk exposure. These best practices provide a strong foundation for a secure digital environment.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep all software and operating systems updated with the latest security patches.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforce strong, unique passwords and implement multi-factor authentication.
- Employee Security Awareness Training: Educate employees about common cyber threats and best security practices.
- Network Security Monitoring: Implement intrusion detection and prevention systems to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Regularly back up data and store it securely offsite to ensure business continuity in case of a breach.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test a comprehensive incident response plan to effectively handle security incidents.
- Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing: Regularly scan your network and systems for vulnerabilities and conduct penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Third-Party Vendor Risk Management: Vet third-party vendors and their security practices before engaging their services.
Understanding Policy Coverage
Cyber insurance policies offer a range of coverages designed to mitigate the financial and operational impacts of cyberattacks and data breaches. Understanding the specifics of these coverages is crucial for selecting a policy that adequately protects your organization. This section will explore the common types of coverage, typical exclusions and limitations, and the variations in coverage limits and deductibles offered by different insurers.
Types of Cyber Insurance Coverage
Cyber insurance policies typically include several key types of coverage. These are not universally included in every policy, and the specific details of each coverage will vary between insurers and policy types. It’s vital to carefully review the policy wording to understand exactly what is and isn’t covered.
- Data Breach Response: This coverage helps cover the costs associated with responding to a data breach, including legal fees, public relations expenses, credit monitoring services for affected individuals, and notification costs. The extent of coverage can vary significantly.
- Business Interruption: This covers the loss of income and extra expenses incurred due to a cyberattack that disrupts business operations. This might include the cost of restoring systems, hiring temporary staff, and lost revenue during downtime.
- Extortion: This coverage can help with ransom payments demanded by cybercriminals in cases of ransomware attacks. However, there are often limitations and conditions placed on this type of coverage, such as requiring law enforcement involvement or proof of the attack’s validity.
- Cyber Liability: This covers third-party claims arising from a data breach, such as lawsuits alleging negligence or failure to protect data. This is a crucial aspect of coverage, as the financial consequences of such lawsuits can be substantial.
- System Restoration: This covers the costs of restoring computer systems and data after a cyberattack. This can include hardware and software replacement, data recovery, and IT consultant fees.
Exclusions and Limitations
While cyber insurance offers valuable protection, it’s essential to be aware of the exclusions and limitations. These clauses specify circumstances where coverage will not be provided. Some common exclusions include:
- Pre-existing conditions: Damage or vulnerabilities known before the policy inception may not be covered.
- Intentional acts: Losses resulting from intentional acts by the insured or their employees are typically excluded.
- War and terrorism: Cyberattacks linked to acts of war or terrorism are often excluded.
- Specific types of malware: Some policies might exclude coverage for certain types of malware or attacks.
- Failure to follow security best practices: Policies may exclude or limit coverage if the insured failed to maintain adequate security measures.
Coverage Limits and Deductibles
Coverage limits represent the maximum amount an insurer will pay for a covered loss. Deductibles are the amount the insured must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. Both vary significantly depending on the insurer, the specific policy, and the risk profile of the insured organization. For example, a small business might have a policy with a $100,000 coverage limit and a $5,000 deductible, while a large corporation might have a multi-million dollar limit and a higher deductible. It’s crucial to carefully consider your organization’s risk profile and budget when selecting coverage limits and deductibles. A higher deductible will typically result in lower premiums, but it means a larger upfront cost in the event of a claim.
The Claims Process
Filing a cyber insurance claim can seem daunting, but understanding the process can significantly ease the burden during a stressful time. A prompt and well-documented claim is crucial for a successful outcome, minimizing financial and operational disruptions. This section Artikels the typical steps involved and factors influencing the claim’s speed and success.
The claims process generally begins with immediate notification to your insurer. This should occur as soon as a cyber incident is detected or suspected. Swift reporting allows the insurer to begin investigating promptly and initiate the necessary response measures. Following the initial notification, a detailed investigation ensues, involving gathering evidence and assessing the extent of the damage. This often requires close collaboration between the policyholder and the insurer’s claims team. Finally, after the investigation, the insurer will assess the claim and determine the amount of coverage to be provided.
Required Documentation During the Claims Process
Providing comprehensive documentation is critical for a smooth and efficient claims process. Incomplete or inaccurate information can significantly delay the claim’s resolution. The specific documents required will vary depending on the nature of the incident and the terms of your policy, but generally include:
- A detailed description of the cyber incident, including the date, time, and method of attack.
- Evidence of the incident, such as system logs, forensic reports, and incident response documentation. This might include screenshots of malware alerts, network traffic logs showing unauthorized access, or reports from security professionals.
- Copies of any relevant contracts or agreements with third-party vendors, particularly if the incident involves a data breach impacting client information.
- Financial records demonstrating the losses incurred as a result of the cyber incident. This might include invoices for remediation services, legal fees, regulatory fines, or lost revenue.
- A completed claims form provided by your insurer. This form will typically request specific details about the incident and the losses incurred.
Factors Affecting Claim Speed and Success
Several factors can influence how quickly and successfully a cyber insurance claim is processed. A proactive approach to risk management and thorough documentation are key to a positive outcome.
- Timeliness of Reporting: Prompt notification is crucial. Delays in reporting can impact the insurer’s ability to effectively investigate and mitigate the damage, potentially leading to claim denials or reduced payouts.
- Policy Coverage: The specific terms and conditions of your cyber insurance policy will dictate the extent of coverage. Understanding your policy’s exclusions and limitations is vital before an incident occurs.
- Quality of Documentation: Comprehensive and accurate documentation is paramount. Lack of evidence or insufficient detail can delay the claims process and potentially lead to a reduced payout.
- Cooperation with the Insurer: Active cooperation with the insurer’s investigation is essential. Failure to provide requested information or cooperate fully can hinder the claims process.
- Incident Response Plan: Having a well-defined incident response plan in place before an incident occurs can significantly improve the speed and efficiency of the claims process. A pre-planned response demonstrates preparedness and minimizes the disruption caused by the incident.
Cost and Value of Cyber Insurance
Cyber insurance, while offering crucial protection, comes with a cost. Understanding the factors influencing premiums and comparing that cost to the potential financial fallout of a cyberattack is vital for making an informed decision. This section will explore the financial aspects of cyber insurance, demonstrating its value as a strategic investment.
The cost of cyber insurance premiums is determined by a range of factors specific to the insured entity. A comprehensive risk assessment is fundamental in determining the appropriate premium. Higher risk profiles naturally lead to higher premiums.
Factors Influencing Cyber Insurance Premiums
Several key factors contribute to the final cost of a cyber insurance policy. These factors are carefully assessed by insurers to accurately reflect the risk they are undertaking. A thorough understanding of these factors allows businesses to better manage their premiums and mitigate risk.
- Industry Sector: Some industries, like finance or healthcare, are inherently more vulnerable to cyberattacks and thus face higher premiums.
- Company Size and Revenue: Larger companies with greater digital assets and more complex IT infrastructure typically pay more.
- Existing Security Measures: Companies with robust cybersecurity measures in place, such as multi-factor authentication and regular security audits, often qualify for lower premiums. This demonstrates a commitment to risk mitigation.
- Data Sensitivity: Handling sensitive personal or financial data significantly increases risk and, consequently, premiums. Regulations like GDPR further amplify this.
- Geographic Location: The prevalence of cybercrime in a specific region can influence premium costs.
- Claims History: A history of previous cyber incidents, even minor ones, can lead to higher premiums in the future.
Comparing Cyber Insurance Costs to Potential Cyberattack Costs
The cost of cyber insurance is often dwarfed by the potential financial consequences of a successful cyberattack. A single breach can result in millions of dollars in losses from various sources. These costs include:
- Data Breach Response Costs: This includes legal fees, forensic investigations, credit monitoring for affected individuals, and public relations efforts.
- Regulatory Fines and Penalties: Non-compliance with data protection regulations can result in substantial fines.
- Business Interruption Losses: A cyberattack can disrupt operations, leading to lost revenue and productivity.
- Reputational Damage: A security breach can severely damage a company’s reputation, impacting customer trust and future business.
- Recovery Costs: Restoring systems and data after an attack can be expensive and time-consuming.
Consider a hypothetical scenario: A small business suffers a ransomware attack, resulting in data encryption and a demand for a $50,000 ransom. Recovery costs, including system restoration and lost business, could easily exceed $100,000. The annual premium for cyber insurance might be significantly less than this total potential cost.
Return on Investment (ROI) of Cyber Insurance
The ROI of cyber insurance is best understood as risk mitigation rather than direct financial return. While premiums are a cost, the potential savings from avoiding the catastrophic expenses of a major cyberattack far outweigh this cost. Cyber insurance provides a financial safety net, allowing businesses to focus on recovery and business continuity rather than financial ruin. The peace of mind it provides, allowing businesses to concentrate on their core operations, also contributes significantly to the overall ROI. The cost of the insurance is a predictable expense; the cost of a cyberattack is not. This predictable cost versus unpredictable, potentially catastrophic cost is the true value proposition.
Cyber Insurance and Compliance
Cyber insurance plays a crucial role in helping organizations navigate the complex landscape of regulatory compliance and demonstrate due diligence to stakeholders. A comprehensive cyber insurance policy can significantly mitigate the financial and reputational risks associated with data breaches and other cyber incidents, thus bolstering an organization’s compliance posture and building trust with investors, customers, and partners.
Cyber insurance can directly assist organizations in meeting regulatory compliance requirements by providing resources and support to address incidents effectively and efficiently. This includes access to incident response teams, legal counsel, and public relations specialists, all of which are critical in managing the fallout from a cyberattack and minimizing regulatory penalties. Furthermore, many policies include coverage for notification costs, which are often mandated by regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Demonstrating the proactive steps taken to secure data and mitigate risks, including holding adequate cyber insurance, strengthens an organization’s position during audits and investigations.
Cyber Insurance and Due Diligence
Possessing adequate cyber insurance demonstrates a commitment to proactive risk management and due diligence to various stakeholders. Investors view cyber insurance as a sign of responsible business practices, reducing their perceived risk and increasing confidence in the organization’s long-term stability. Customers and partners also benefit from knowing that the organization has taken steps to protect their data and minimize the impact of potential breaches. This transparency builds trust and strengthens business relationships. For example, a healthcare provider with robust cyber insurance demonstrates to patients and regulators a commitment to protecting sensitive medical information, reinforcing compliance with HIPAA regulations. A financial institution with comprehensive cyber insurance coverage shows its commitment to protecting customer financial data, meeting regulatory requirements like those imposed by the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA).
Industry-Specific Regulations and Cyber Insurance
Various industries face unique regulatory landscapes that significantly impact their cyber insurance needs. For instance, the healthcare industry, governed by HIPAA in the United States, faces stringent requirements for protecting patient health information (PHI). A breach of PHI can result in significant fines and reputational damage. Cyber insurance policies tailored to the healthcare industry typically include coverage for HIPAA-related breaches, including notification costs, legal fees, and regulatory fines. Similarly, the financial services industry, subject to regulations like GLBA and GDPR, requires comprehensive cyber insurance to address the potential for financial loss and reputational harm from data breaches impacting customer financial information. These policies often cover regulatory fines, remediation costs, and business interruption expenses. The payment card industry, governed by PCI DSS, faces significant penalties for non-compliance. Cyber insurance can help mitigate these risks by covering costs associated with achieving and maintaining PCI DSS compliance, including audits and remediation efforts. Failing to obtain and maintain appropriate cyber insurance in these highly regulated sectors can expose organizations to substantial financial and legal liabilities.
Future Trends in Cyber Insurance
The cyber insurance landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks and the proliferation of interconnected devices. Future trends reflect a move towards more proactive risk management, leveraging advanced technologies, and expanding coverage to address emerging threats. This necessitates a shift in how both insurers and businesses approach cyber risk.
The impact of evolving technologies on cyber insurance is profound. AI and machine learning are transforming risk assessment, claims processing, and fraud detection, leading to more accurate pricing and efficient operations. Simultaneously, the expanding attack surface, fueled by the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and artificial intelligence itself, requires insurers to adapt their policies to encompass these new vulnerabilities.
AI-Powered Risk Assessment and Predictive Modeling
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the way cyber risk is assessed. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets, including network traffic, security logs, and vulnerability scans, to identify patterns and predict potential threats with greater accuracy than traditional methods. This allows insurers to offer more tailored policies based on a granular understanding of an organization’s specific risk profile. For example, an AI system might identify a company’s weak points in its patch management system and flag this as a high-risk factor, leading to a higher premium or a recommendation for specific security enhancements. This predictive modeling can also assist in identifying potential future threats, allowing insurers and businesses to proactively mitigate risks.
Extended Coverage for Emerging Threats
Cyber insurance policies are expanding to cover emerging threats such as ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS), supply chain attacks, and deepfakes. RaaS, which allows even unsophisticated actors to launch devastating ransomware attacks, necessitates coverage that extends beyond traditional data breach response. Supply chain attacks, targeting vulnerabilities in an organization’s third-party vendors, require policies that account for the broader ecosystem. Similarly, deepfakes, synthetic media that can be used for identity theft or disinformation campaigns, require specialized coverage to address the unique risks they pose. For instance, a policy might now include coverage for legal fees associated with defending against accusations based on a deepfake.
The Rise of Cyber Insurance Platforms and APIs
The integration of cyber insurance with other security tools and platforms is becoming increasingly common. Insurers are developing APIs and platforms that allow seamless integration with security information and event management (SIEM) systems, threat intelligence platforms, and vulnerability management tools. This facilitates real-time risk monitoring, automated claims processing, and proactive risk mitigation. This integration enables a more holistic approach to cyber risk management, allowing for faster response times and improved overall security posture. A company’s security system could automatically notify its insurer of a breach, triggering an immediate response and expediting the claims process.
Focus on Prevention and Proactive Risk Management
The cyber insurance industry is shifting its focus from solely reactive measures to a more proactive approach. Insurers are increasingly incentivizing preventative measures through risk-based pricing and offering discounts for organizations that implement robust security controls. This encourages businesses to invest in preventative security measures, leading to a reduction in overall cyber risk and a more sustainable insurance market. For example, a company with a strong security posture, including multi-factor authentication and regular security audits, may qualify for a lower premium.
Cyber Insurance for Small Businesses
Small businesses, the backbone of many economies, are increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks. While often lacking the extensive IT resources of larger corporations, they face significant risks from data breaches, ransomware attacks, and other cyber threats that can cripple their operations and lead to substantial financial losses. Cyber insurance provides a crucial safety net, offering financial protection and support in the face of these challenges. This guide helps small business owners understand the importance of cyber insurance and how to choose the right policy.
Unique Cyber Risks Faced by Small Businesses
Small businesses often possess limited cybersecurity expertise and budgets, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. They may rely on outdated software, lack robust security protocols, and have fewer employees dedicated to IT security. This vulnerability translates into a higher likelihood of experiencing data breaches, malware infections, phishing attacks, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. These incidents can lead to financial losses from downtime, legal fees, regulatory fines, and the cost of recovering data and systems. Furthermore, the reputational damage caused by a security breach can be devastating for a small business, potentially driving away customers and impacting future growth. Cyber insurance helps mitigate these risks by providing financial coverage for the costs associated with these incidents.
Choosing the Right Cyber Insurance Policy for Small Businesses
Selecting the appropriate cyber insurance policy requires careful consideration of several factors. Small businesses should first assess their specific risks and vulnerabilities. This involves identifying critical data assets, evaluating existing security measures, and considering potential threats. Once a risk assessment is complete, businesses can begin comparing policies. Key factors to consider include coverage limits for data breach response, business interruption, regulatory fines, and legal fees. Policy exclusions, deductibles, and the insurer’s reputation and claims handling process should also be carefully examined. It’s advisable to work with an independent insurance broker who can help navigate the complexities of the market and find a policy that best fits the business’s needs and budget.
The Importance of Cyber Insurance in Protecting Small Business Data and Operations
Cyber insurance offers crucial protection for small businesses by covering the financial burden associated with cyberattacks. This includes costs related to data recovery, system restoration, legal and regulatory fees, and public relations efforts to mitigate reputational damage. Beyond financial protection, a comprehensive cyber insurance policy often includes access to valuable resources such as incident response teams and cybersecurity experts who can guide businesses through the recovery process. This support can be invaluable in minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity following a cyber incident. Furthermore, having cyber insurance can demonstrate to customers and partners a commitment to data security, enhancing trust and reputation.
Cyber Insurance Cost and Value for Small Businesses
The cost of cyber insurance for small businesses varies significantly depending on factors such as industry, revenue, the number of employees, and the level of coverage. While premiums can represent an added expense, the potential cost of a cyberattack far outweighs the cost of insurance in most cases. A single data breach can cost a small business tens of thousands, or even hundreds of thousands, of dollars. Cyber insurance acts as a cost-effective risk management tool, transferring the financial burden of a cyber incident to the insurer while providing access to crucial support services. The value of cyber insurance lies in its ability to protect a small business’s financial stability, reputation, and operational continuity in the face of escalating cyber threats.
Clarifying Questions
What types of businesses benefit most from cyber insurance?
Businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large corporations, can benefit from cyber insurance. The specific coverage needs will vary depending on the size, industry, and data handling practices of the business.
How much does cyber insurance cost?
The cost of cyber insurance varies greatly depending on factors such as the size of the business, industry, level of risk, and the amount of coverage desired. It’s crucial to obtain quotes from multiple providers to compare costs and coverage.
What is the claims process like?
The claims process typically involves reporting the incident to your insurer, providing necessary documentation (e.g., police reports, incident reports), and cooperating with the insurer’s investigation. The speed and success of the claim depend on several factors, including the policy terms and the completeness of the information provided.
Can cyber insurance cover legal fees?
Many cyber insurance policies include coverage for legal fees associated with data breaches, regulatory investigations, or lawsuits arising from a cyberattack. The specific coverage will vary depending on the policy.